In this article, we will cover how to create a Workload Identity that works with GitHub Actions while deploying a simple Google Cloud Run service.
GitHub has recently introduced the OIDC tokens as part of GitHub Actions Workflow, so now you can authenticate from GitHub Actions to Google Cloud using Workload Identity Federation, and no longer use JSON service account keys.
Prerequisites
- A GitHub account with a repository created
- A Google Cloud account with Billing enabled
- The Google Cloud CLI installed and authenticated
Create a Hello World service
For the purposes of testing, we will create a basic web service in Python using FastAPI and Uvicorn.
1. Using your favorite editor, create an main.py with the following content:
from fastapi import FastAPI
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/")
async def root():
return {"message": "Hello World"}
2. Create a requirements.txt file listing the following dependencies:
fastapi
uvicorn3. Create a Dockerfile file that will be used to build the image for the service:
FROM python:3
WORKDIR /app
COPY . .
RUN pip install -r requirements.txt
EXPOSE 8080
CMD ["uvicorn", "main:app", "--host", "0.0.0.0", "--port", "8080"]4. (Optional) You can test the image locally, assuming Docker is installed, by:
docker build . -t app
docker run -p 8080:8080 app
curl http://localhost:8080
(out){"message":"Hello World"}
5. Commit and push the code to your GitHub repository.
git add main.py requirements.txt Dockerfile
git commit -m "Create Hello World service"
git push
Create a Google Cloud Project
1. If you don't have one already, create a new project on the Google Cloud Platform.
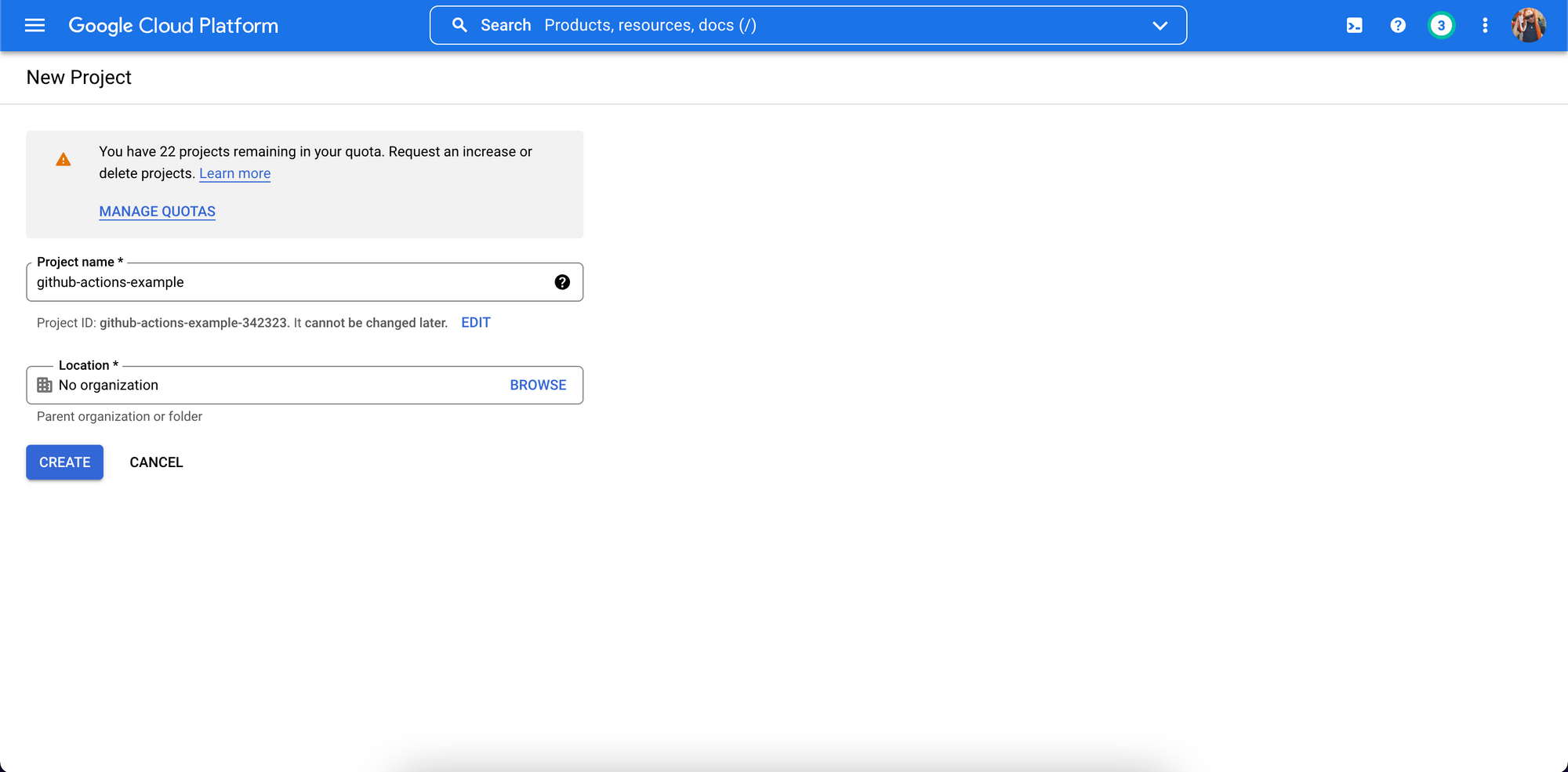
2. Take a note of the Project ID, in this example github-actions-example-342323.
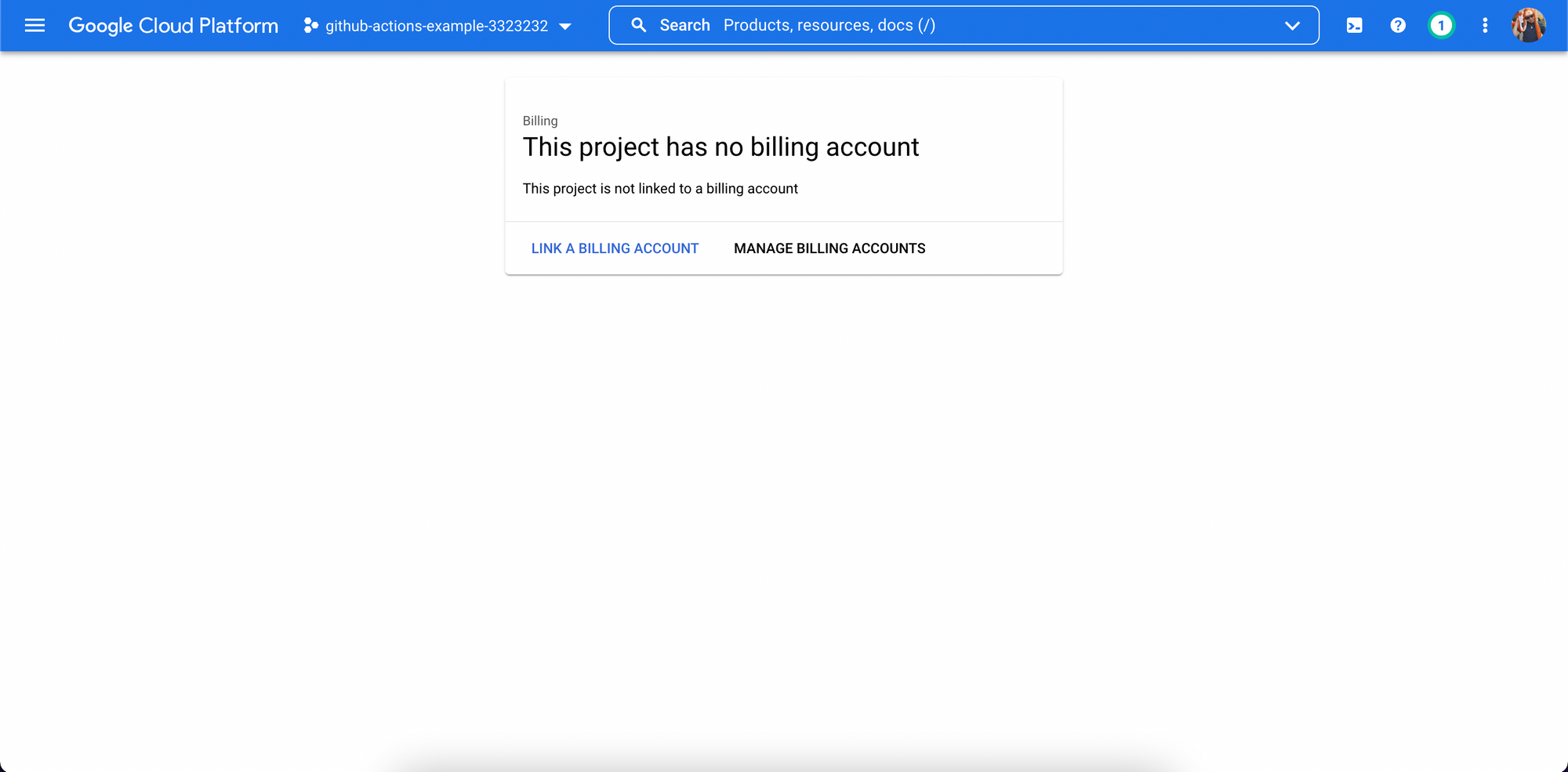
3. Visit the Navigation Menu, then Billing to make sure there's a billing account linked to the project.
Create a Workload Identity on Google Cloud
While most of the configuration can be made on Google Cloud Console, from now on, we will only use the gcloud command to make the chances needed.
1. To make things easier, we will set temporary variables in our terminal session:
ForSERVICE_ACCOUNT,WORKLOAD_IDENTITY_POOLandWORKLOAD_IDENTITY_PROVIDER, you can use the same values as I did, or come up with your own.
export GITHUB_REPO=$YOUR_GITHUB_REPO$ (e.g. user/project)
export PROJECT_ID=$YOUR_PROJECT_ID$
export SERVICE_ACCOUNT=github-actions-service-account
export WORKLOAD_IDENTITY_POOL=gh-pool
export WORKLOAD_IDENTITY_PROVIDER=gh-provider
2. Now, using the gcloud command, set the project:
gcloud config set project $PROJECT_ID
3. Enable the APIs for Artifact Registry, IAM Credential, Container Registry and Cloud Run:
gcloud services enable \
(out) artifactregistry.googleapis.com \
(out) iamcredentials.googleapis.com \
(out) containerregistry.googleapis.com \
(out) run.googleapis.com
4. Create a Service Account that will be used by GitHub Actions:
gcloud iam service-accounts create $SERVICE_ACCOUNT \
(out) --display-name="GitHub Actions Service Account"
5. Bind the Service Account to the Roles in the Services it must interact:
gcloud projects add-iam-policy-binding $PROJECT_ID \
(out) --member="serviceAccount:$SERVICE_ACCOUNT@$PROJECT_ID.iam.gserviceaccount.com" \
(out) --role="roles/iam.serviceAccountUser"
gcloud projects add-iam-policy-binding $PROJECT_ID \
(out) --member="serviceAccount:$SERVICE_ACCOUNT@$PROJECT_ID.iam.gserviceaccount.com" \
(out) --role="roles/run.developer"
gcloud projects add-iam-policy-binding $PROJECT_ID \
(out) --member="serviceAccount:$SERVICE_ACCOUNT@$PROJECT_ID.iam.gserviceaccount.com" \
(out) --role="roles/storage.admin"
6. Create a Workload Identity Pool for GitHub:
gcloud iam workload-identity-pools create $WORKLOAD_IDENTITY_POOL \
(out) --location="global" \
(out) --display-name="GitHub pool"
7. Create a Workload Identity Provider for GitHub:
gcloud iam workload-identity-pools providers create-oidc $WORKLOAD_IDENTITY_PROVIDER \
(out) --location="global" \
(out) --workload-identity-pool=$WORKLOAD_IDENTITY_POOL \
(out) --display-name="GitHub provider" \
(out) --attribute-mapping="google.subject=assertion.sub,attribute.actor=assertion.actor,attribute.repository=assertion.repository" \
(out) --issuer-uri="https://token.actions.githubusercontent.com"
8. Retrieve the Workload Identity Pool ID:
WORKLOAD_IDENTITY_POOL_ID=$(gcloud iam workload-identity-pools \
(out) describe $WORKLOAD_IDENTITY_POOL \
(out) --location="global" \
(out) --format="value(name)")
9. Allow authentications from the Workload Identity Provider originating from your repository:
gcloud iam service-accounts add-iam-policy-binding \
(out) $SERVICE_ACCOUNT@$PROJECT_ID.iam.gserviceaccount.com \
(out) --role="roles/iam.workloadIdentityUser" \
(out) --member="principalSet://iam.googleapis.com/${WORKLOAD_IDENTITY_POOL_ID}/attribute.repository/${GITHUB_REPO}"
10. Finally, extract the Workload Identity Provider resource name:
WORKLOAD_IDENTITY_PROVIDER_LOCATION=$(gcloud iam workload-identity-pools providers \
(out) describe $WORKLOAD_IDENTITY_PROVIDER \
(out) --location="global" \
(out) --workload-identity-pool=$WORKLOAD_IDENTITY_POOL \
(out) --format="value(name)")
Create a GitHub Actions Workflow
We will create a simple workflow that can be triggered by new changes on the main branch, pull requests or manual dispatch. This workflow will create a new Google Cloud Run service called app and will run a simple curl test on the service.
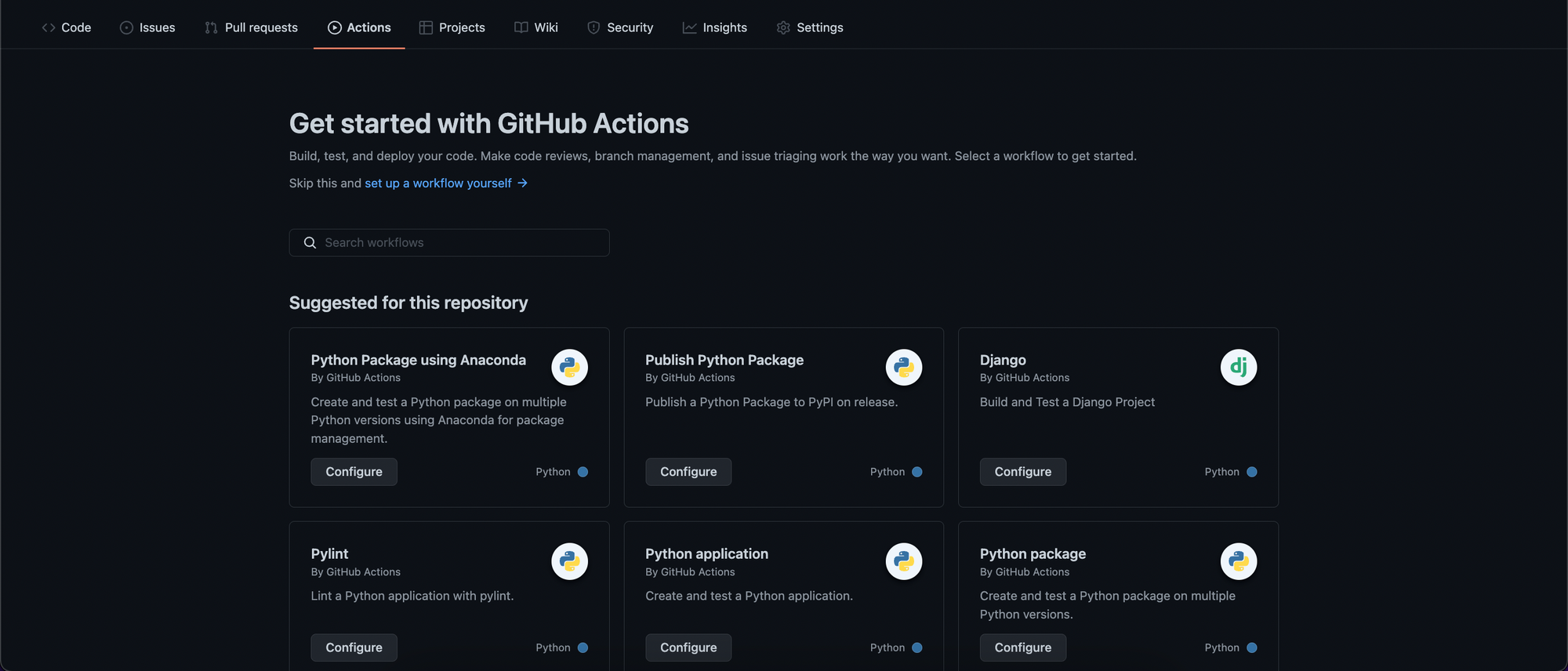
1. Head over to your GitHub Project, go to Actions, then click on set up a workflow yourself:
2. Before we edit the main.yml file, let's recover some variables from our terminal session:
echo $WORKLOAD_IDENTITY_PROVIDER_LOCATION
(out)(e.g.) projects/21710762087/locations/global/workloadIdentityPools/gh-pool/providers/gh-provider
echo $SERVICE_ACCOUNT@$PROJECT_ID.iam.gserviceaccount.com
(out)(e.g.) github-actions-service-account@github-actions-example-342323.iam.gserviceaccount.com
3. Now, using the values from above, replace them in the file below and submit the changes on GitHub by clicking on the Start commit button.
# This is a basic workflow to help you get started with Actions
name: CD
# Controls when the workflow will run
on:
# Triggers the workflow on push or pull request events but only for the main branch
push:
branches: [main]
pull_request:
branches: [main]
# Allows you to run this workflow manually from the Actions tab
workflow_dispatch:
# A workflow run is made up of one or more jobs that can run sequentially or in parallel
jobs:
# This workflow contains a single job called "deploy"
deploy:
# The type of runner that the job will run on
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
# Add "id-token" with the intended permissions.
permissions:
contents: "read"
id-token: "write"
env:
# Replace $PROJECT_ID with your project ID
IMAGE_NAME: gcr.io/$PROJECT_ID/app
# Steps represent a sequence of tasks that will be executed as part of the job
steps:
# Checks-out your repository under $GITHUB_WORKSPACE, so your job can access it
- name: Checkout repository
uses: actions/checkout@v2
- name: Authenticate to Google Cloud
uses: google-github-actions/auth@v0
with:
# Replace with your Workload Identity Provider Location
workload_identity_provider: "$WORKLOAD_IDENTITY_PROVIDER_LOCATION"
# Replace with your GitHub Service Account
service_account: "$SERVICE_ACCOUNT@$PROJECT_ID.iam.gserviceaccount.com"
- name: Configure Docker
run: gcloud auth configure-docker --quiet
- name: Build Docker image
run: docker build . -t $IMAGE_NAME
- name: Push Docker image
run: docker push $IMAGE_NAME
- id: deploy
name: Deploy Docker image
uses: "google-github-actions/deploy-cloudrun@v0"
with:
image: ${{ env.IMAGE_NAME }}
region: us-central1
service: app
flags: --port=8080
# Example of using the output
- name: Test URL
run: curl "${{ steps.deploy.outputs.url }}"4. Almost immediately after submitting you can see a new workflow run under the Actions tab. If everything goes well your service will be deployed:
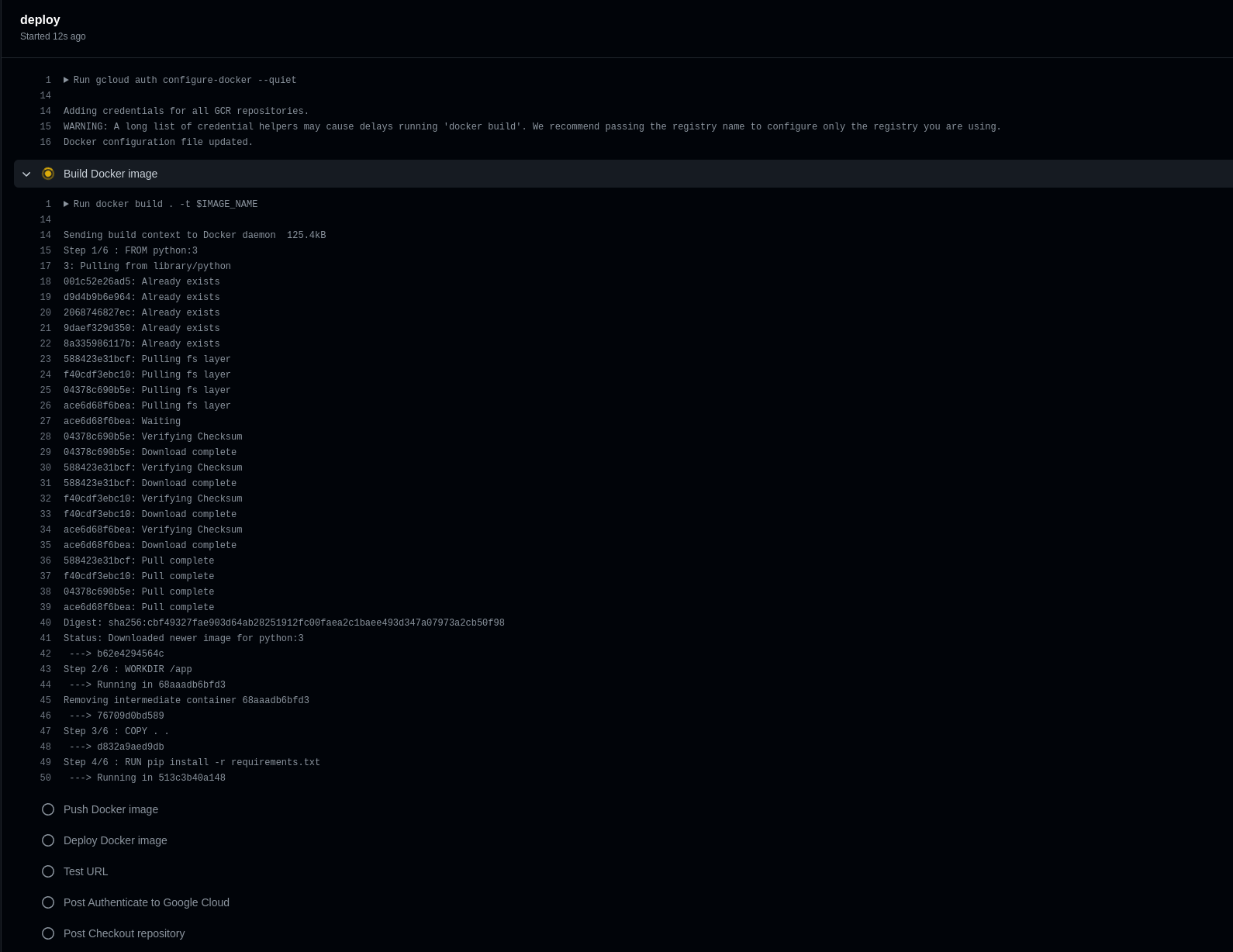
That's it! Now, any new changes in your repository will trigger a new deploy action.
Tip: Allowing anyone to access the Google Cloud Run service
You may have noticed that if the Cloud Run service was deploy for the first time using google-github-actions/deploy-cloudrun@v0, it will give you an 403 Forbidden when you try to access its URL.
If it's your intention to make it public, and available to everyone with access to your service URL, you can simply fix it by adding allUsers as run.invoker to your service:
gcloud run services add-iam-policy-binding app \
(out) --member="allUsers" \
(out) --role="roles/run.invoker"
Ta-da!

